There are a number of ways in which food can affect our bodies. It can give us energy, impact how we feel, and change our health. Foods can have both positive and adverse affects, so it’s important that we look at what we’re eating. One of those adverse affects can be an inflammatory response. Inflammation is the body’s attempt to remove something harmful or irritating. Why would you want to eat something that elicits this sort of reaction? You probably wouldn’t. That’s why I’ve gathered this list of 12 inflammatory foods, so you can cut out what the cause might be.
Table of Contents
Sugar

Sugar consumption, even in low to moderate levels, can promote inflammation, particularly in sweetened beverages. Excessive sugar intake is also linked to inflammation markers, diabetes, and heart disease.
Avoid refined sugars and limit how much sugar you consume in your diet. Try swapping out sugar for honey instead. Naturally sweet foods like fruits can be a great alternative for a sweet tooth.
Aspartame
As with sugar, this artificial sweetener can lead to inflammation. Aspartame isn’t recognized by the body the same way as natural sweeteners are. This can lead to an allergic response from the body, causing swelling, headaches, and hives.
Just say no to artificial sweeteners. Diet soda and other foods made with aspartame are putting your health at risk. Cane sugar in moderation is still better than an artificial sweetener, though both are inflammatory foods.
MSG
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) is an excitotoxin that tricks your brain to think food is more flavorful. It’s hidden in up to 90 ingredients, so even if you think you’ve been avoiding it, chances are you haven’t. Not only can inflammation occur as a result of the high sodium content of MSG, but also from an allergic response from the body.
MSG doesn’t occur in whole fruits and vegetables. It’s only in processed foods. In general, anything with a flavor packet or seasoning is likely to contain MSG in some form, so your best to avoid it.
Alcohol
Research has shown a link between alcohol consumption and inflammation, especially with regular alcohol use. Frequent alcohol consumption can disrupt the intestinal lining, letting bacteria pass into the bloodstream, leading to inflammation.
If avoiding alcohol all together isn’t a likely option for you, stick to less than 2 drinks a day and opt for wine instead, as it contains more antioxidants.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Although these fatty acids are important for your health, they must be balanced with the amount of Omega-3 fatty acids we consume. American’s tends to have more Omega-6s in their diets, due to the high consumption of corn, soy, and cottonseed oils. The imbalance of Omega-3s and Omega-6s triggers an inflammatory response.
Stick to oils with a lower content of Omega-6s and oils that contain oleic acid, such as olive oil. It acts as an anti-inflammatory.
Trans Fats
The concern over trans fats is nothing new. They can lead to inflammation, high cholesterol, obesity, and cancer. In women, consumption of trans fatty acids can lead to systemic inflammation. You’ll find trans fats in certain baked goods, snacks, fried food, margarine, and other processed foods.
Luckily, you can see if a food contains trans fats by looking at the nutrition label, so it’s one of the most easily avoidable inflammatory foods on this list. The FDA began requiring this in 2006 in an attempt to limit the amount of trans fats in food. They are no longer generally regarded as safe by the FDA either.
Saturated Fats
Saturated fats are usually in grain fed animal products. Just like trans fats, they are linked to pro-inflammatory markers. Certain oils can be high in saturated fats, like coconut and palm oils. However unrefined coconut oil, for example, also has anti-inflammatory properties.
Avoid processed foods high in saturated fat, such as pizza, sausage, and grain-based desserts. You can find out the saturated fat content of a food by looking at the nutrition label.
Refined Grains
Research is beginning to show that refined grains have pro-inflammatory effects, which is why we regard them as inflammatory foods. High-glycemic starches can trigger inflammation, so things like white bread and white rice are foods you should avoid.
The same research indicates that whole grains may reduce inflammation. Choose ancients grains, like quinoa or amaranth instead of rice. Use whole grain flour and look for complete whole grains when shopping.
Grain-Fed Beef
You’ve heard the saying, you are what you eat. Conventional beef comes from cows fed conventional grains; the same grains that are likely to cause inflammation. This grain-fed beef is also high in Omega-6 fatty acids, which we’ve already labeled as a trigger for inflammation. There is also some science indicating a particular sugar in in large quantities of red meat can contribute to inflammation as well.
Opt for grass-fed beef instead. The elimination of a grain diet that is used to fatten up the cow helps to eliminate the inflammation factor. Choosing to eat less red meat is also a way to reduce inflammation risk. You may want to try the addition of meatless Mondays.
Hydrogenated Oils/Vegetable Oils
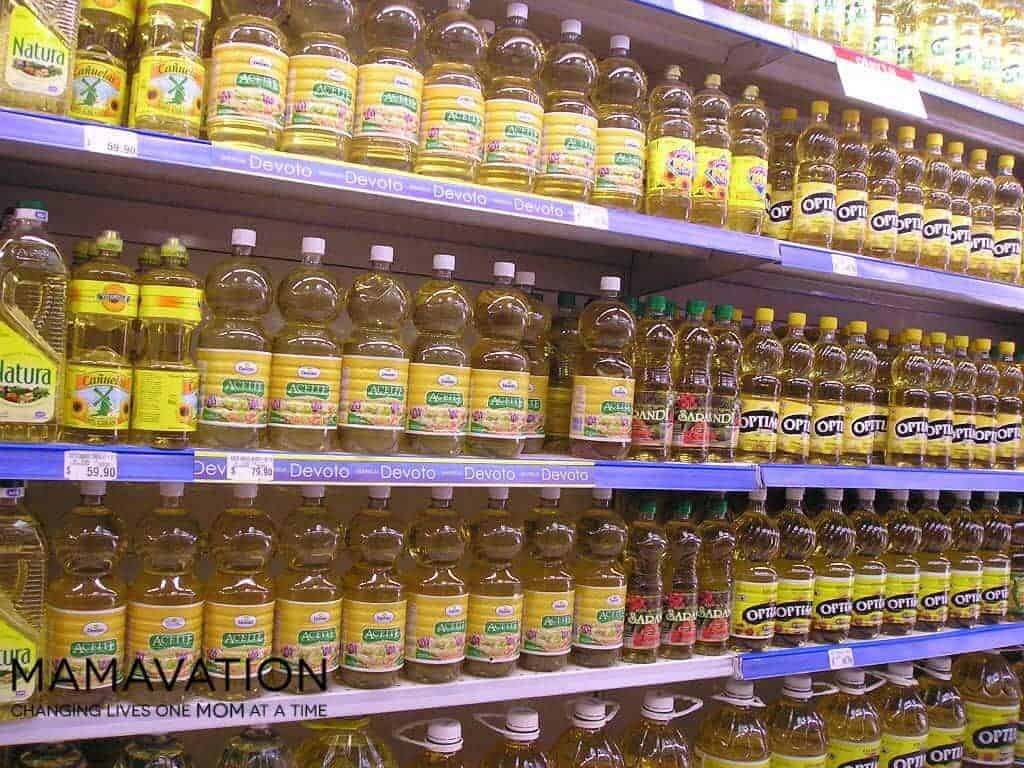

We’ve already discussed the high levels of Omega-6 fatty acids in vegetable oils, these oils still make the list on their own. Hydrogenated oils are linked to cancer, and the way vegetable, corn, soy, and cottonseed oils, just to name a few, are processed is cause for concern. A study found home use of vegetable oils elevated inflammatory biomarkers.
When you’re deciding what oil to use, try olive oil or coconut oil. They are both anti-inflammatory and have a number of health benefits.
Gluten
For those with Celiac disease or gluten intolerance, eating gluten is a can lead to an inflammatory response. The body sees gluten as a foreign invader and attacks it, causing inflammation. It’s estimated that 10% of the population is gluten intolerant.
A gluten-free diet has been show to reduce inflammation. If you suspect you have a problem digesting the protein gluten, switching to a gluten-free diet may help to determine if that is indeed what is causing your inflammation and possible gastrointestinal issues.
Dairy
In some people, dairy can illicit an inflammatory response caused by the sugars and proteins in milk. Those who are lactose intolerant don’t have the enzyme required to break down the sugars in milk, lactose. Casein, one of the proteins in milk, can also cause some people to react unfavorably. Those who are gluten intolerant may also have an inflammatory response to dairy.
If you’re sensitive to dairy, and find it to be one of the inflammatory foods that affects you, you may want to try raw milk instead. It contains an enzyme that helps to digest lactose. The digestion of lactose in turn produces lactic acid which helps to digest milk proteins.
Chronic Inflammation
So why all the concern over inflammation? A little swelling doesn’t seem like a big deal, right? Acute inflammation is our body’s way to heal and protect us after injury. Chronic inflammation is when the body repeatedly pumps out cytokines as part of an inflammatory response. That leads to a constant state of inflammation in the body’s tissue. This chronic inflammation only gets worse with age and leads to more problems and disease. Chronic inflammation is linked to cancer, diabetes, heart disease, allergies, and depression. All the more reason to consider the contributing factors to inflammation in your life.
Do you think any of these possibly inflammatory foods could because causing you to suffer from inflammation?



 Dangerous Disposable Dinnerware: Toxic Dinnerware that Destroys the Earth
Dangerous Disposable Dinnerware: Toxic Dinnerware that Destroys the Earth
Great topic and article. Thank you for posting this! I suffer from an autoimmune disease and am always trying to eat accordingly to reduce inflammation. It’s a struggle but this definitely helps with my list of “don’ts”!
Such a great overview of what inflammation means, what causes it and why we need to pay attention to it. I have been suspecting that some of these foods are issues for me…. now I need to take action. Thank you for this plethora of knowledge, Elizabeth.